Arbitrum and Polygon are Layer 2 (L2) networks created to solve efficiency and scalability problems plaguing the Ethereum blockchain. Since Ethereum is one of the largest and most used networks, developers create projects that help to scale the network for faster transactions and reduced gas fees.
An in-depth comparison of both L2 scaling solutions is important for potential users as well as investors. And this article will do just that – go over the main differences & similarities between ARB & MATIC.
Let’s begin with the basics… 👇
What is Arbitrum (ARB)?
Arbitrum was created to complement Ethereum by boosting transaction speed, privacy, and scalability. It is an L2 solution that scales the Ethereum blockchain by processing transactions off the network.

Who created Arbitrum?
Former Princeton Computer Science and Public Relations professor Ed Felten created Offchain Labs in 2018 and launched Arbitrum with Harry Kalodner and Steven Goldfeder. Felten also worked as the Deputy Chief Technology officer at the White House from 2015 to 2017. In a Nasdaq interview in 2022, Felten confirmed that the idea came in 2014 when Princeton academics realized Web3 would come with fundamental challenges, such as cost and speed.
Key Features of Arbitrum
Arbitrum has gained popularity as an effective scaling solution because of the following features:
- Low Fees: Arbitrum boasts affordable transaction fees that are currently (May 2023) approximately 20 times cheaper compared to Ethereum Mainnet.
- Easy for Developers: To significantly minimize its entry barriers, Arbitrum was designed to allow developers to use it with existing Ethereum toolset, without needing to use any Arbitrum-specific compilers or plugins.
- EVM Compatibility: Arbitrum is compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) at the bytecode level. This ensures ease of use for everyone already familiar with Ethereum programming languages.
What is Polygon (MATIC)?
Polygon is an L2 Ethereum scaling solution. Like Arbitrum, Polygon facilitates transactions at cheaper costs while scaling the Ethereum network to accommodate more transactions. The solution structurally enhances Ethereum by providing added interoperability and security to the network via the Polygon Bridge, which helps to independently process transactions off-chain.

Who created Polygon?
Polygon, formerly known as The Matic Network, began in 2017 when Housing.com data scientist, Jaynti Kanani, noticed congestion on the Ethereum blockchain, largely from the Cryptokitties NFT project. Kanani then created a solution with business consultant Anurag Arjun and blockchain developer Sandeep Nailwal, launching The Matic Network in the same year.
Key Features of Polygon
Users of the Polygon network enjoy the following features:
- Increased Speed: Polygon makes the Ethereum network more scalable. Applications can process transactions faster and offer users a smoother experience.
- Cost-Effective: Polygon users enjoy lower transaction fees since it can process transactions off-chain without congesting Ethereum.
- Staking: Users can stake Polygon’s native token MATIC to secure the network and earn an average annual percentage yield (APY) of up to 20%.
ARB vs MATIC: Transaction Speed
Arbitrum and Polygon both increase transaction speed from a few transactions per second to several thousand. However, while Arbitrum can take speeds to about 40,000 transactions per second (TPS), Polygon can process nearly 200% of Arbitrum’s speed, at nearly 65,000 TPS.
The Arbitrum solution uses optimistic rollups, a compression method that “rolls up” a batch of transactions into one. This way, the network processes several transactions at once rather than tackling each one individually.
Instead of sticking to one option, Polygon combines multiple scaling methods to accommodate more transactions. Polygon uses optimistic rollups, zero knowledge (ZK) rollups, and sidechain technology. Using a sidechain allows Polygon to run alongside Ethereum and securely exchange data and assets. Like Arbitrum, Polygon also uses optimistic rollups to batch transactions and process them together. However, Polygon also uses ZK rollups, which ensure security by applying zero-knowledge proof verification for each transaction.
ARB vs MATIC: Scalability
While they are both largely successful, Polygon achieves a larger throughput than Arbitrum. Polygon also hosts more than 19,000 dApps, much higher than the 200+ live projects on Arbitrum.
Polygon and Arbitrum realize scalability using methods that also help attain impressive transaction speeds. Polygon uses a sidechain, and also applies optimistic and ZK rollups to bundle multiple transactions. Like Polygon, Arbitrum also rolls up transactions to scale the Ethereum network.
ARB vs MATIC: Security
Layer 2 solutions have security features rooted in the Layer 1 blockchain. For instance, the rollup solution requires that transactions begin as calldata on the L1, even though processing happens on L2. Therefore, regardless of L2 activity, anyone can access and retrieve L1 data.
There also is the AnyTrust security feature Arbitrum uses to ensure that honest verifiers properly execute L2 transactions despite efforts from dishonest parties. This keeps the network safe and protects against security risks.
Polygon assures network security through staking. In addition to primary calldata available on the Ethereum blockchain, Polygon uses MATIC tokens for security. By staking MATIC, users make the network more resilient and invulnerable. In addition to staking, Polygon creates checkpoints on Ethereum as it processes transactions, each checkpoint ensuring that all prior processing is complete and safe for Ethereum.
ARB vs MATIC: Ecosystem & Development
Since 2017, Polygon has improved developer interactions with Ethereum so much that it announced more than 19,000 dApps as of April 2022. Some popular Polygon dApps include Uniswap V3, OpenSea, and the 1inch Network.
In addition, social media giant Meta chose Polygon to power minting and trading digital collectibles on Instagram. Polygon also hosts more than 60 metaverse projects, including Decentraland and The Sandbox. As of May 6, 2023, Polygon’s total value locked (TVL) sits at $997,26 million, according to multi-chain dashboard DefiLlama. TVL measures the total value of assets on a network or platform and is a good indicator of public trust.
Arbitrum has also had its fair share of numbers. For instance, the project completed three investment rounds between 2019 and 2021, receiving $123.7 million. Arbitrum launched its mainnet in August 2021 and now hosts over 270 dApps, including AAVE, Curve, and SushiSwap.
Arbitrum’s TVL is much higher than Polygon’s at $2.44 billion as of May 6, 2023. This figure has climbed nearly 48% in less than 2 months, from the $1.53 billion recorded in March.
ARB vs MATIC: Tokenomics
Let’s look at some important parameters of both ARB and MATIC tokens to get a better understanding of where they stand compared to the rest of the crypto market.
The tokenomics of MATIC
Polygon’s tokenomics system is more complex and features two tokens – MATIC and Quickswap (QUICK). MATIC handles network functions, including staking and governance, while QUICK is used to reward liquidity providers.
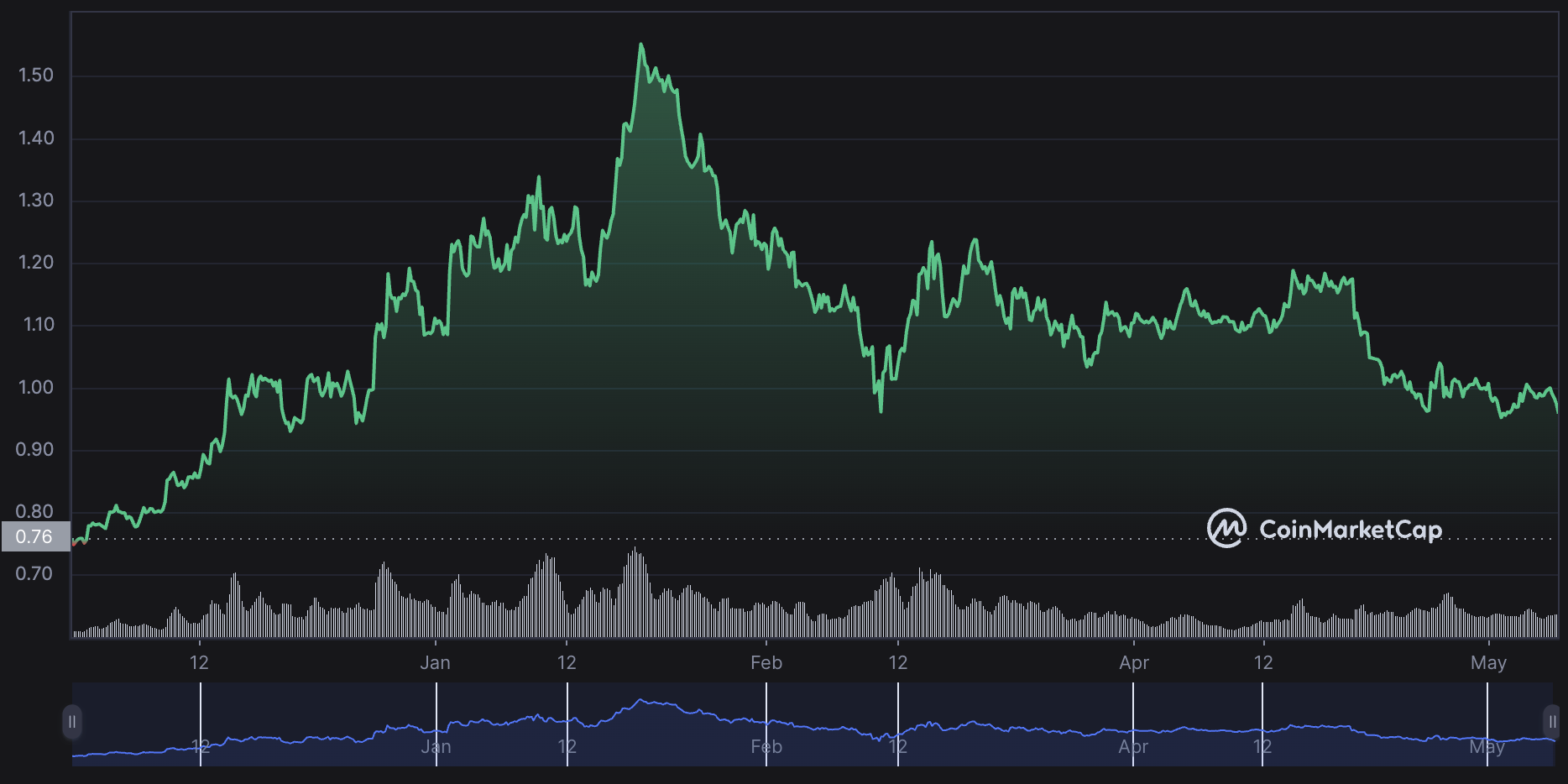
MATIC price chart in 2023. Source: CoinMarketCap
Polygon launched MATIC on April 26, 2019, with an initial supply of 10 billion tokens. The initial distribution allocated the three largest portions at 23.33%, 21.86%, and 19.00% to the ecosystem, foundation, and Binance Launchpad.
As of May 6, 2023, MATIC has a market cap of $8.883 billion, daily volume of $363 million, and 9.24 billion MATIC in circulating supply,
The tokenomics of ARB
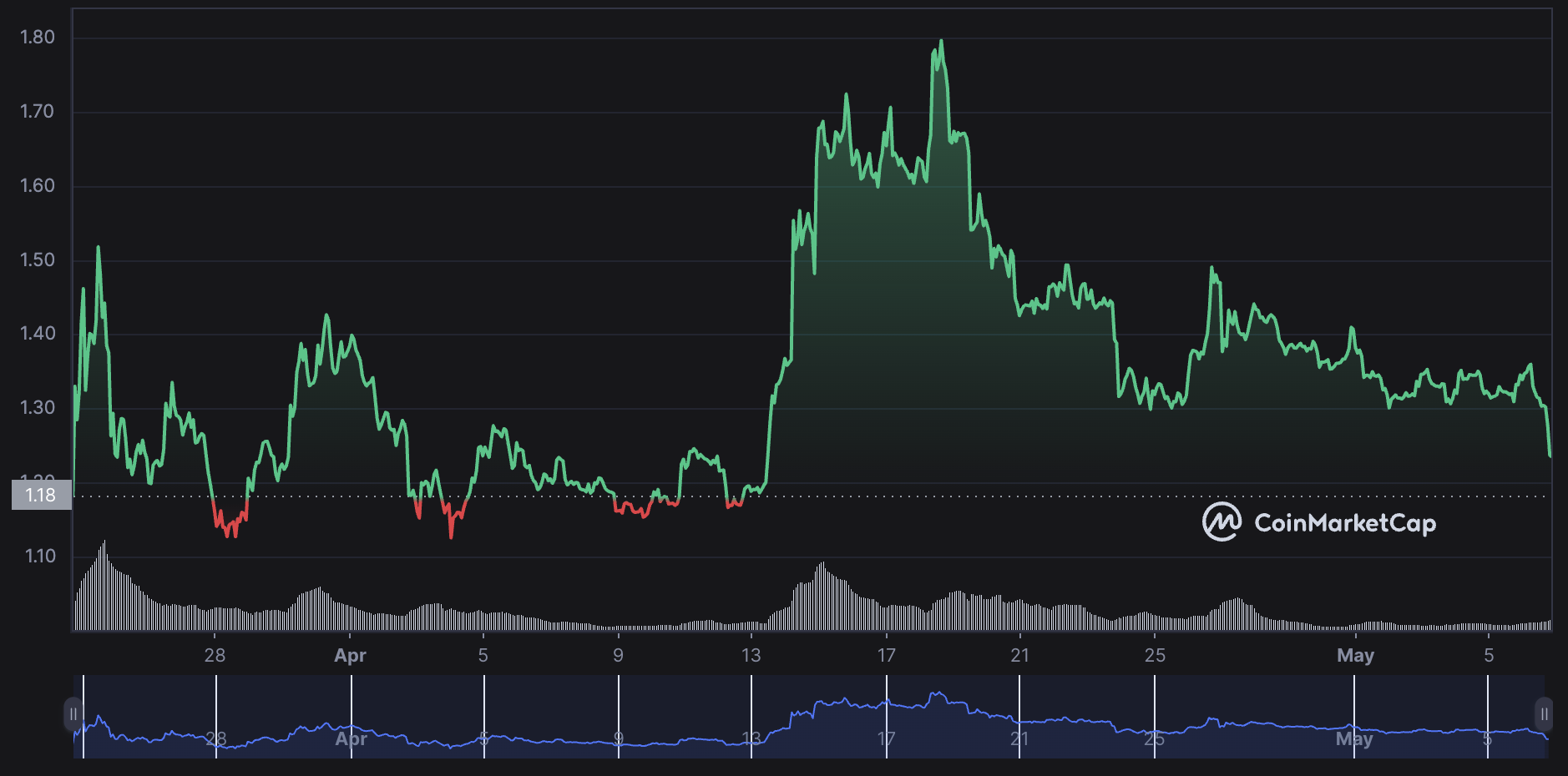
ARB price chart in 2023. Source: CoinMarketCap
Arbitrum’s tokenomics is different. There’s only the ARB token, initially designed to handle internal operations on the network. However, Arbitrum distributed 12.75% of its 10 billion supply to eligible recipients on March 23, 2023. The airdrop marked Arbitrum’s transition to a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO), allowing ARB holders to vote on ecosystem decisions.
As of May 6, ARB has a market cap of $1.57 billion, daily volume of $455 million, and a circulating supply of 1.275 billion ARB.
ARB vs MATIC: Price Prediction
ARB is trading at $1.23 after gaining about 10% over the last week. Regardless, it is the 37th largest cryptocurrency by market cap, notwithstanding its 88% crash from its initial launch price of $11.8, according to CoinMarketCap.
Cryptopredictions.com predicts that by the end of 2023, ARB’s average price, after the initial swings wear off, is predicted to hit $1.613, with $2 as its potential maximum and $1.37 as the minimum. These increases should hold for a while, with $1.72 as the average price in 2024, and $2.3 in 2025. The price of ARB should rise over 132% to $3.017 in 2027.
MATIC is currently bearish, dropping about 5% to $0.9589 over the past 7 days. Since ARB’s airdrop, MATIC has fallen over 15% from $1.1370.
Nevertheless, Cryptopredictions expect MATIC to hit an average price of $1.108 by the end of 2023, with a $1.385 maximum and a $0.94 minimum. The token’s 2025 average price should rise to $1.856 and to $2.48 in 2027.
Of course, you must remember to always do your own research and not rely solely on predictions available on different online resources.
ARB vs MATIC: Investment potential
ARB and MATIC have considerable potential, having a solid use case and considerable community support.
Polygon has the potential to process more transactions than other L2 solutions and already has the highest number of daily transactions. Polygon’s scalability accommodates a large NFT market – something that Arbitrum can’t boast about. In addition, Polygon has partnered with Reddit, allowing users to buy NFT profile pictures and store them in Reddit’s Vault crypto wallet.
This is not to say that Arbitrum has nothing going for it. Its TVL is almost double that of Polygon’s. In fact, Arbitrum’s TVL is higher than the cumulative TVL of Arbitrum and Optimism (another popular Ethereum scaling solution).
This goes to show the value its users see in Arbitrum protocol. TVL is also an important signifier of a protocol’s well-being, reflecting its strength and current potential.
How to buy ARB and MATIC
There are many ways to invest into both of these cryptocurrencies. However, we recommend you check out Guardarian for some of the best deals on the market.
With us you can buy ARB, MATIC and 1000+ other cryptocurrencies with any major payment method, such as credit/debit cards, bank transactions or Google Pay.
We also don’t require registration – the entire process only takes a couple minutes!
Simply follow these steps:
- Go to www.guardarian.com.
- Choose the crypto you want to buy and what you are paying with and click “Buy”.
- Enter your desired wallet address.
- Complete a quick & intuitive checkout process – no registration needed!
- Check your wallet & we hope to see you soon. 😉
Alternatively, you can visit the designated pages we have for both ARB and MATIC & make the buying process even faster.

Conclusion
Deciding on the better investment option may depend on several factors, including individual preferences and risk tolerance. People with some risk appetite may choose to invest in ARB since it only became available recently and may have a lot of growth potential. Risk-averse investors may prefer MATIC as it is older and because Polygon can handle many more transactions.
For individual preference, the choice may boil down to optimistic and ZK rollups, transaction speed of both platforms, or their tokenomics. Either way, it is crucial to pay close attention to their metrics, such as fluctuations in daily transaction numbers, and TVL. Nevertheless, Arbitrum and Polygon will likely stick around for as long as the Ethereum blockchain requires third-party options to improve scalability.
We hope that this article gave you a better view of the differences between ARB & MATIC. Visit our website for some amazing crypto deals & make sure to follow us on X for the latest crypto news & educational articles! ✨




